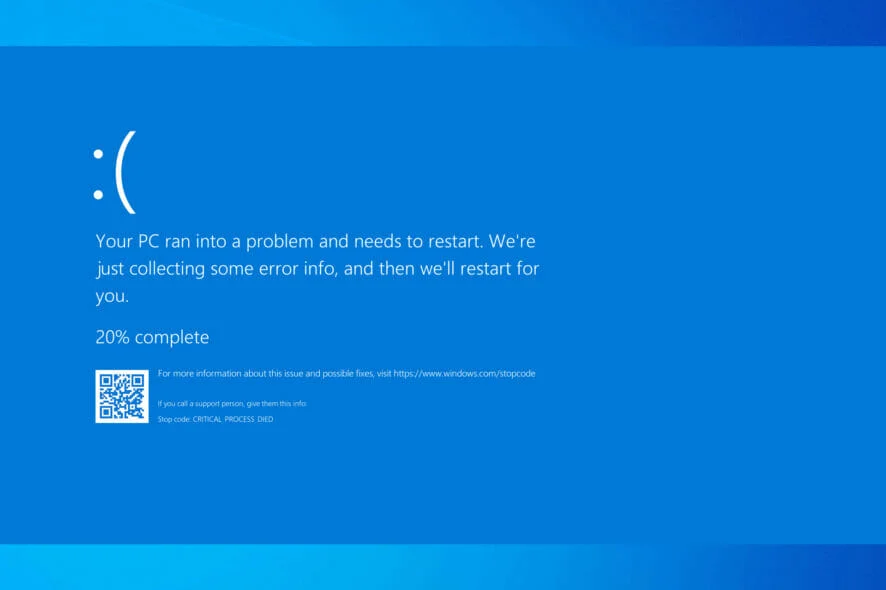
The DRIVER_VERIFIER_DMA_VIOLATION error is a type of Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) that occurs in Windows 11 when the Driver Verifier tool detects a violation related to Direct Memory Access (DMA). DMA is a feature that allows hardware devices to access system memory directly, bypassing the CPU. When a driver misbehaves during DMA operations, it can lead to system instability, resulting in this specific BSOD error.
This error is particularly challenging because it often points to issues with third-party drivers or hardware components.
What Causes the DRIVER_VERIFIER_DMA_VIOLATION Error?
The primary cause of this error is a faulty or incompatible driver that mismanages DMA operations. Common culprits include outdated or corrupted drivers for hardware components like graphics cards, network adapters, or storage controllers. Additionally, hardware issues such as faulty RAM or incompatible peripherals can also trigger this error.
Another potential cause is the misuse of the Driver Verifier tool itself. While this tool is designed to identify problematic drivers, enabling it without proper configuration can sometimes lead to false positives or system instability. Therefore, it’s crucial to use this tool judiciously and only when necessary.
Step 1: Boot into Safe Mode
Before attempting any fixes, it’s advisable to boot your system into Safe Mode. This mode loads only the essential drivers and services, allowing you to troubleshoot without interference from third-party software. To enter Safe Mode, restart your computer and press F8 or Shift + F8 during the boot process. Alternatively, you can access Safe Mode through the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE).
Once in Safe Mode, you can begin diagnosing the issue. Check for any recently installed drivers or hardware that might be causing the problem. If the error doesn’t occur in Safe Mode, it’s a strong indication that a third-party driver is to blame.
Step 2: Use the Driver Verifier Tool
The Driver Verifier tool is a built-in Windows utility designed to identify problematic drivers. To use it, open the Command Prompt as an administrator and type verifier. This will launch the Driver Verifier Manager. Select Create custom settings and choose the options related to DMA verification.
After configuring the settings, restart your computer. The tool will monitor your drivers and flag any that violate DMA protocols. If a problematic driver is identified, you’ll receive a BSOD with detailed information about the offending driver. Make a note of the driver name and proceed to update or uninstall it.
Step 3: Update or Roll Back Drivers
If the Driver Verifier tool identifies a specific driver, the next step is to update or roll back that driver. Open the Device Manager by right-clicking the Start menu and selecting it from the list. Locate the problematic driver, right-click it, and choose Update driver. If an update is available, install it and restart your computer.
If updating the driver doesn’t resolve the issue, consider rolling back to a previous version. Right-click the driver in Device Manager, select Properties, and navigate to the Driver tab. Click Roll Back Driver if the option is available. This can often resolve compatibility issues that lead to DMA violations.
Step 4: Perform System Diagnostics
If driver updates or rollbacks don’t resolve the issue, it’s time to perform a comprehensive system diagnostic. Use tools like Windows Memory Diagnostic to check for RAM issues or CHKDSK to scan for hard drive errors. These tools can help identify underlying hardware problems that might be contributing to the DMA violation.
Additionally, consider running the System File Checker (SFC) and DISM tools to repair corrupted system files. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type sfc /scannow followed by DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth. These commands can fix system file corruption that might be causing the BSOD error.
Step 5: Disable Driver Verifier
Once you’ve identified and resolved the issue, it’s important to disable the Driver Verifier tool to prevent further BSOD errors. Open Command Prompt as an administrator and type verifier /reset. This will turn off the Driver Verifier and allow your system to boot normally.
If you continue to experience issues, consider performing a clean boot to isolate the problem further. This involves disabling all non-essential startup programs and services, allowing you to identify any software conflicts that might be causing the DMA violation.