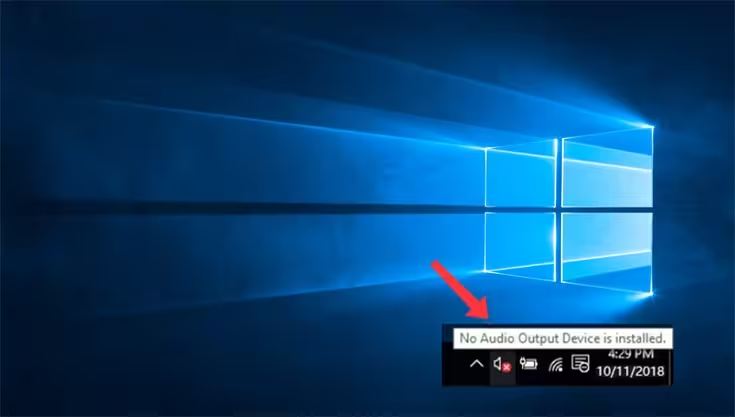
The “No Audio Output Device is Installed” error often arises due to outdated or corrupted audio drivers. Drivers act as intermediaries between your operating system and hardware, ensuring seamless communication. When these drivers malfunction, your system may fail to recognize audio devices. Additionally, misconfigured sound settings or disabled audio devices can trigger this error.
Hardware issues, such as disconnected cables or faulty audio hardware, can also contribute to the problem. However, software-related causes are more common and easier to address.
Step 1: Check Device Manager for Audio Drivers
The Device Manager is a critical tool for managing hardware components and their drivers. To begin troubleshooting:
- Press Windows + X and select Device Manager from the menu.
- Expand the Sound, video, and game controllers section.
- Look for your audio device (e.g., Realtek High Definition Audio). If it has a yellow exclamation mark, the driver may be outdated or corrupted.
If the audio device is missing entirely, it could indicate a hardware disconnection or a deeper driver issue. Right-click the device and select Update driver to search for updates automatically. Alternatively, visit the manufacturer’s website to download the latest driver manually.
Step 2: Reinstall or Roll Back Audio Drivers
If updating the driver doesn’t resolve the issue, consider reinstalling it. In the Device Manager:
- Right-click the audio device and select Uninstall device.
- Restart your computer. Windows will attempt to reinstall the driver automatically.
Alternatively, if the issue started after a recent driver update, rolling back to a previous version may help. In the Device Manager, right-click the audio device, select Properties, go to the Driver tab, and click Roll Back Driver.
Step 3: Verify Sound Settings
Incorrect sound settings can also cause the error. To check:
- Right-click the speaker icon in the taskbar and select Sounds.
- Go to the Playback tab and ensure your audio device is set as the default.
- If the device is disabled, right-click it and select Enable.
If no devices appear, your system may not detect any audio hardware. This could indicate a deeper issue, such as a hardware failure or a missing driver.
Step 4: Run the Audio Troubleshooter
Windows 11 includes a built-in troubleshooter that can automatically detect and fix common audio issues. To use it:
- Open Settings and navigate to System > Troubleshoot > Other troubleshooters.
- Click Run next to Playing Audio.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the process.
The troubleshooter can identify and resolve issues such as disabled devices, incorrect settings, or driver conflicts.
Step 5: Check for Windows Updates
Windows updates often include fixes for known bugs and compatibility issues. To ensure your system is up to date:
- Open Settings and go to Windows Update.
- Click Check for updates and install any available updates.
After updating, restart your computer and check if the audio issue is resolved. Updates can address driver incompatibilities and improve system stability.
Step 6: Inspect Hardware Connections
If software troubleshooting doesn’t resolve the issue, inspect your hardware. For desktop users:
- Ensure your speakers or headphones are properly connected to the correct audio jack.
- Check for loose cables or damaged ports.
For laptop users, external audio devices may require additional configuration. If using Bluetooth headphones, ensure they are paired correctly and set as the default playback device.