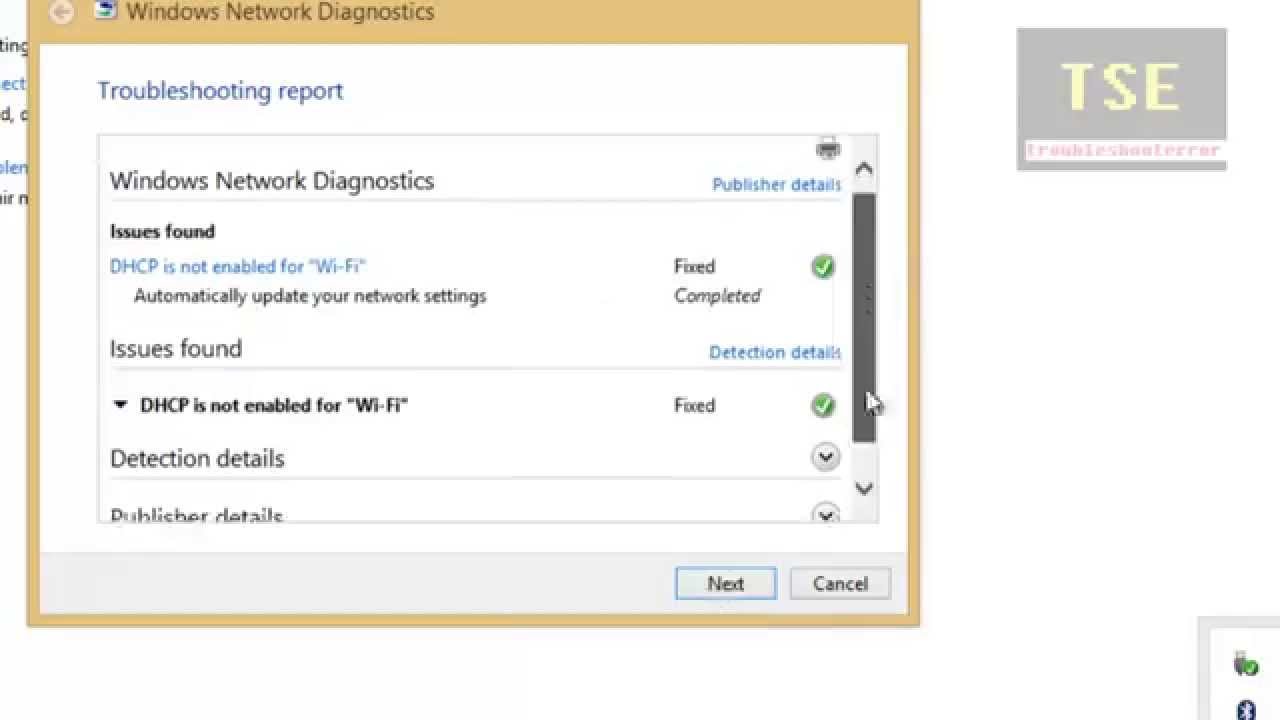
When you encounter the error message ‘DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi,’ it indicates that your Windows device is unable to automatically obtain an IP address from your router. This issue can disrupt your internet connectivity, making it essential to resolve it promptly.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is a network management protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices on a network. Without DHCP enabled, your device cannot communicate effectively with the router, leading to connectivity issues.
Understanding DHCP and Its Role in Wi-Fi Connectivity
DHCP is a critical component of modern networking. It automates the process of assigning IP addresses, subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS servers to devices on a network. When DHCP is not enabled, your device cannot receive these essential network parameters, resulting in the ‘DHCP is not enabled for Wi-Fi’ error. This issue often arises due to misconfigured router settings, disabled DHCP on the network adapter, or incorrect network configurations.
Step 1: Verify Router DHCP Settings
The first step in resolving the DHCP error is to check your router’s DHCP settings. Access your router’s admin panel by entering its IP address (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1) into a web browser. Log in using your admin credentials, which are typically found on the router or in its manual.
Once logged in, navigate to the DHCP settings section. Ensure that the DHCP server is enabled. If it is disabled, enable it and save the changes. Restart your router to apply the new settings.
- Access your router’s admin panel via its IP address.
- Log in using admin credentials.
- Navigate to the DHCP settings section.
- Enable the DHCP server if it is disabled.
- Save changes and restart the router.
Step 2: Enable DHCP on Your Windows Network Adapter
If your router’s DHCP settings are correct, the next step is to ensure that your Windows network adapter is configured to obtain an IP address automatically.
To do this, open the Network and Sharing Center by right-clicking the network icon in the system tray and selecting ‘Open Network & Internet settings.’ Click on ‘Change adapter options,’ then right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select ‘Properties.’ In the Properties window, select ‘Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)’ and click ‘Properties.’ Ensure that both ‘Obtain an IP address automatically’ and ‘Obtain DNS server address automatically’ are selected. Click ‘OK’ to save the changes.
- Open the Network and Sharing Center.
- Click ‘Change adapter options.’
- Right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and select ‘Properties.’
- Select ‘Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)’ and click ‘Properties.’
- Ensure ‘Obtain an IP address automatically’ and ‘Obtain DNS server address automatically’ are selected.
Step 3: Reset TCP/IP and Winsock Catalog
If the above steps do not resolve the issue, resetting the TCP/IP stack and Winsock catalog can help. Open Command Prompt as an administrator by searching for ‘cmd’ in the Start menu, right-clicking on it, and selecting ‘Run as administrator.’ In the Command Prompt window, type the following commands one by one, pressing Enter after each:
netsh int ip resetnetsh winsock reset
After executing these commands, restart your computer. This process resets the network configurations to their default state, which can resolve issues caused by corrupted settings.
Step 4: Update or Reinstall Network Adapter Drivers
Outdated or corrupted network adapter drivers can also cause DHCP-related errors. To update your drivers, open Device Manager by pressing Windows + X and selecting ‘Device Manager.’ Expand the ‘Network adapters’ section, right-click your Wi-Fi adapter, and select ‘Update driver.’ Choose ‘Search automatically for updated driver software.’
If no updates are found, consider downloading the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website and installing them manually. If updating the drivers does not work, uninstall the adapter, restart your computer, and let Windows reinstall the drivers automatically.
- Open Device Manager.
- Expand ‘Network adapters’ and right-click your Wi-Fi adapter.
- Select ‘Update driver’ and choose automatic search.
- If no updates are found, download drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
- Uninstall the adapter and restart your computer if necessary.
Step 5: Disable Conflicting Third-Party Software
Third-party software, such as VPNs, firewalls, or network management tools, can interfere with DHCP functionality. Temporarily disable or uninstall such software to determine if it is causing the issue. If the error is resolved after disabling the software, consider using an alternative program or adjusting its settings to avoid conflicts with DHCP.
- Identify and disable third-party VPNs, firewalls, or network tools.
- Uninstall conflicting software if necessary.
- Test your Wi-Fi connection after disabling the software.