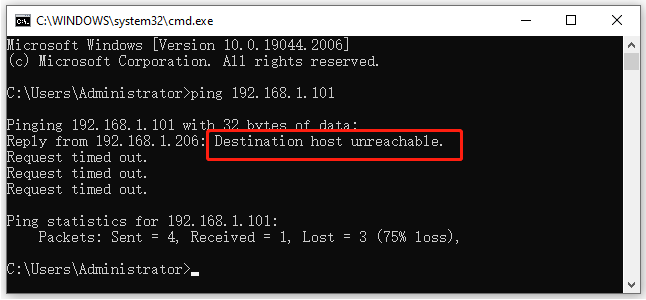
The ‘Destination Host Unreachable’ error in Windows is a common network issue that disrupts connectivity, often caused by misconfigured network settings, router problems, or restrictive firewall rules. This error indicates that your device cannot establish a connection to the intended destination, which could be another device on your local network or an external server.
To diagnose the problem, you can use the ping command in the Command Prompt. If the response includes ‘Destination Host Unreachable,’ it confirms that the issue lies in the network path or the destination device itself.
Verify Network Configurations
Incorrect network configurations are a leading cause of this error. Start by checking your IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway settings. These can be verified using the ipconfig command in the Command Prompt. Ensure that your device has a valid IP address and that the subnet mask and gateway align with your network’s requirements.
- Open Command Prompt and type ipconfig.
- Check the IPv4 Address, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway.
- Compare these values with your network’s expected settings.
If the settings are incorrect, you can manually configure them or use the netsh command to reset your network adapter. Additionally, ensure that your DNS settings are properly configured, as incorrect DNS entries can also lead to connectivity issues.
Check Router Settings
Your router plays a critical role in facilitating communication between devices on your network and external servers. If the router is misconfigured, it can block traffic and cause the ‘Destination Host Unreachable’ error. Start by rebooting your router to clear any temporary glitches. If the issue persists, log in to your router’s admin interface to inspect its settings.
- Access your router’s admin panel using its IP address (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Verify that the DHCP server is enabled to assign IP addresses automatically.
- Check for any blocked IP addresses or ports in the firewall settings.
If you suspect that the router’s firmware is outdated, consider updating it to the latest version. Firmware updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements that can resolve connectivity issues.
Adjust Firewall Rules
Firewalls are designed to protect your system from unauthorized access, but overly restrictive rules can block legitimate traffic and cause the ‘Destination Host Unreachable’ error. Start by checking your Windows Firewall settings to ensure that the necessary ports and protocols are allowed.
- Open Windows Defender Firewall from the Control Panel.
- Navigate to ‘Advanced settings’ and review the inbound and outbound rules.
- Ensure that rules for essential services like ICMP (used by ping) are enabled.
If you are using a third-party firewall, consult its documentation to adjust the rules accordingly. Temporarily disabling the firewall can help identify if it is the source of the problem, but remember to re-enable it after testing.
Test Connectivity After Changes
After making the necessary adjustments, test your connectivity using the ping command again. If the ‘Destination Host Unreachable’ error no longer appears, your changes were successful. If the issue persists, consider additional troubleshooting steps such as resetting your TCP/IP stack or performing a network reset in Windows.
To reset the TCP/IP stack, open Command Prompt as an administrator and run the following commands:
- netsh int ip reset
- ipconfig /release
- ipconfig /renew
These commands will reset your network configurations to their default state, potentially resolving any lingering issues.