Packet loss is a common network issue that can significantly degrade your internet experience, causing slow speeds, lag, and even disconnections. On Windows 10 and 11, diagnosing and resolving packet loss requires a systematic approach, involving network diagnostics, driver updates, and router configuration adjustments.
Understanding Packet Loss
Packet loss occurs when data packets traveling across a network fail to reach their destination. This can happen due to various reasons, such as network congestion, faulty hardware, or outdated drivers. On Windows, packet loss manifests as slow internet speeds, choppy video calls, or interrupted online gaming sessions.
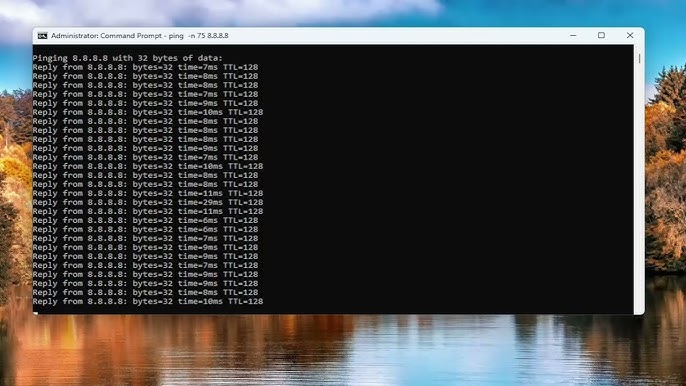
To determine if you’re experiencing packet loss, you can use built-in tools like Ping or PathPing. These tools send data packets to a specified address and measure the response time and packet loss percentage. A packet loss rate above 1-2% is considered problematic and requires further investigation.
Using Network Diagnostic Tools
Windows provides several tools to diagnose network issues, including packet loss. The Command Prompt is your primary tool for running diagnostic tests. Here’s how to use it:
- Open Command Prompt by typing cmd in the Windows search bar and pressing Enter.
- Type ping [target address] -t (e.g., ping google.com -t) and press Enter. This sends continuous packets to the target address.
- Monitor the results for any lost packets. Press Ctrl + C to stop the test.
For a more detailed analysis, use PathPing. This tool combines the functionality of Ping and Traceroute, providing a comprehensive overview of network performance. Run pathping [target address] in Command Prompt to identify where packet loss is occurring along the network path.
Updating Network Drivers
Outdated or corrupted network drivers are a common cause of packet loss. To ensure your drivers are up to date:
- Open Device Manager by right-clicking the Start menu and selecting it from the list.
- Expand the Network adapters section.
- Right-click your network adapter and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for drivers and follow the on-screen instructions.
If Windows doesn’t find an update, visit the manufacturer’s website to download the latest driver manually. Installing the correct driver can resolve compatibility issues and improve network performance.
Adjusting Router Settings
Your router plays a critical role in network performance. Incorrect settings or outdated firmware can lead to packet loss. To optimize your router:
- Access your router’s admin panel by entering its IP address in a web browser (commonly 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Check for firmware updates in the Administration or Maintenance section.
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS) to prioritize traffic for specific applications, such as gaming or video streaming.
- Change the wireless channel to reduce interference from other networks.
If you’re using a dual-band router, connect to the 5 GHz band for faster speeds and less interference. Additionally, ensure your router is placed in a central location to maximize coverage.
Testing and Verifying Fixes
After implementing the above steps, it’s essential to verify whether the packet loss issue has been resolved. Re-run the Ping or PathPing tests to check for improvements. If packet loss persists, consider the following:
- Test your connection with a different device to rule out hardware issues.
- Contact your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to check for network outages or infrastructure problems.
- Replace faulty network cables or hardware, such as routers or modems.
By systematically addressing potential causes, you can effectively resolve packet loss and enjoy a stable, high-performance network connection.