Sleep mode is a power-saving state designed to conserve energy while allowing users to quickly resume their work. Modern power management systems in Windows rely on a combination of hardware and software configurations. When a PC wakes up unexpectedly, it is often due to misconfigured power settings, scheduled tasks, or external devices sending wake signals.
Diagnosing the Cause of Random Wake-Ups
Before attempting to fix the issue, it is crucial to diagnose the root cause. Windows provides built-in tools to help identify what is waking your PC from sleep mode. One of the most effective methods is using the Command Prompt to generate a detailed report.
To generate a power report, follow these steps:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type
powercfg /lastwakeand press Enter. This command will show the last device or process that woke your PC. - For a more comprehensive analysis, type
powercfg /sleepstudy. This generates an HTML report detailing wake events over the past three days.
These reports can reveal whether the issue is caused by a specific device, application, or scheduled task. Once the culprit is identified, you can take targeted action to resolve the problem.
Adjusting Power Settings to Prevent Wake-Ups
Windows power settings play a significant role in managing sleep mode behavior. Misconfigured settings can lead to unintended wake-ups. To address this, you can modify the power plan settings to ensure your PC stays asleep when it should.
Follow these steps to adjust power settings:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to Power Options.
- Select your current power plan and click Change plan settings.
- Click Change advanced power settings to open the advanced settings window.
- Expand the Sleep section and disable Allow wake timers under both On battery and Plugged in settings.
Disabling wake timers prevents scheduled tasks, such as Windows Update or maintenance tasks, from waking your PC. This simple adjustment can significantly reduce random wake-ups.
Disabling Unwanted Wake Timers
Wake timers are a common cause of random wake-ups. These timers allow certain tasks, such as system updates or backups, to wake your PC from sleep mode. While they can be useful, they are often unnecessary and can be disabled without impacting system functionality.
To disable wake timers:
- Open the Task Scheduler by typing
taskschd.mscin the Run dialog (Win + R). - Navigate through the list of tasks and identify those with wake timers enabled.
- Right-click on a task, select Properties, and go to the Conditions tab.
- Uncheck the box labeled Wake the computer to run this task.
By disabling wake timers for non-essential tasks, you can ensure your PC remains in sleep mode until you manually wake it.
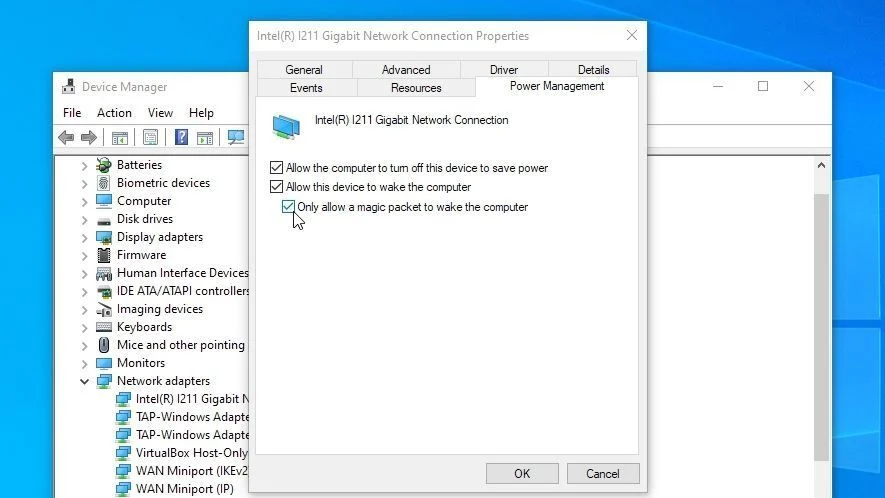
Managing External Devices and Wake Signals
External devices, such as keyboards, mice, and network adapters, can send wake signals to your PC. These signals are often triggered by accidental movements or network activity. To prevent this, you can configure your device settings to disable wake capabilities.
To manage device wake settings:
- Open Device Manager by typing
devmgmt.mscin the Run dialog. - Expand the relevant device category (e.g., Keyboards or Network adapters).
- Right-click on a device and select Properties.
- Go to the Power Management tab and uncheck Allow this device to wake the computer.
This adjustment ensures that only intentional actions, such as pressing the power button, will wake your PC.
Updating Drivers and Firmware
Outdated or incompatible drivers and firmware can also cause random wake-ups. Ensuring that your system is up to date is a critical step in resolving sleep mode issues.
To update drivers and firmware:
- Open Device Manager and check for devices with a yellow exclamation mark, indicating a driver issue.
- Right-click on the device and select Update driver.
- Alternatively, visit the manufacturer’s website to download the latest drivers and firmware.
Keeping your system updated not only resolves sleep mode issues but also improves overall performance and security.
Exploring Advanced Solutions
If the above steps do not resolve the issue, you may need to explore advanced solutions. These include modifying registry settings or using third-party tools to manage power settings more granularly.
For example, you can use the PowerCfg command-line tool to analyze and configure power settings in greater detail. However, these methods should be approached with caution, as incorrect configurations can lead to system instability.