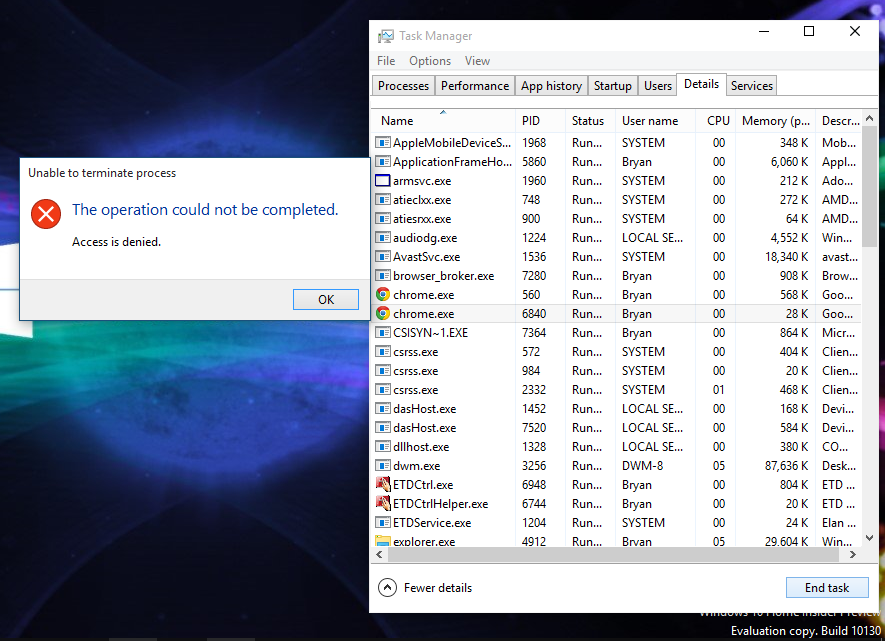
When attempting to end a process or task in Windows 11 Task Manager, encountering an Access Denied error can be frustrating. This error typically indicates that you lack the necessary permissions to terminate the process.
Windows 11 employs a robust security framework that restricts certain actions to protect system integrity. Processes tied to critical system functions or those owned by other users often require elevated permissions to modify or terminate. If you’re not logged in as an administrator or lack the appropriate privileges, Task Manager will block your attempt with an Access Denied message.
Running Task Manager as an Administrator
One of the simplest ways to resolve Access Denied errors is to run Task Manager with elevated privileges. Here’s how:
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager.
- Click on More details if Task Manager is in compact mode.
- Navigate to the File menu and select Run new task.
- Type taskmgr and check the box for Create this task with administrative privileges.
- Click OK to relaunch Task Manager with elevated permissions.
This method grants Task Manager the necessary permissions to terminate protected processes.
Modifying System Permissions
If running Task Manager as an administrator doesn’t resolve the issue, you may need to adjust system permissions manually. Follow these steps:
- Right-click on the process you wish to terminate and select Go to details.
- In the Details tab, right-click the process and choose Open file location.
- Right-click the executable file and select Properties.
- Navigate to the Security tab and click Edit.
- Select your user account and check the box for Full control under Permissions.
- Click Apply and then OK to save changes.
This approach ensures you have full control over the process, allowing you to terminate it without encountering Access Denied errors.
Disabling User Account Control (UAC)
User Account Control (UAC) is a security feature in Windows 11 that restricts unauthorized changes to the system. While it enhances security, it can also cause Access Denied errors. Temporarily disabling UAC can help resolve the issue:
- Press Win + R, type msconfig, and press Enter.
- Go to the Tools tab and select Change UAC settings.
- Click Launch and move the slider to Never notify.
- Click OK and restart your computer.
Remember to re-enable UAC after resolving the issue to maintain system security.
Using Command Prompt to Terminate Processes
If Task Manager fails to terminate a process, you can use Command Prompt with administrative privileges. Here’s how:
- Press Win + S, type cmd, and select Run as administrator.
- Type tasklist and press Enter to view running processes.
- Identify the Process ID (PID) of the task you want to terminate.
- Type taskkill /PID [PID] /F and press Enter.
This command forcefully terminates the process, bypassing Access Denied restrictions.
Checking for Malware or Corrupted Files
In some cases, Access Denied errors may result from malware or corrupted system files. Running a thorough scan can help identify and resolve these issues:
- Use Windows Security or a trusted antivirus program to scan your system for malware.
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator and run sfc /scannow to check for corrupted files.
- If issues are found, restart your computer to apply repairs.
Addressing these underlying problems can prevent recurring Access Denied errors in Task Manager.