Experiencing 100% disk usage on your Windows 11 system can significantly hinder performance, causing slow response times and system freezes. This issue often stems from excessive background processes, outdated drivers, or suboptimal system settings. Addressing this requires a systematic approach to identify and resolve the underlying causes.
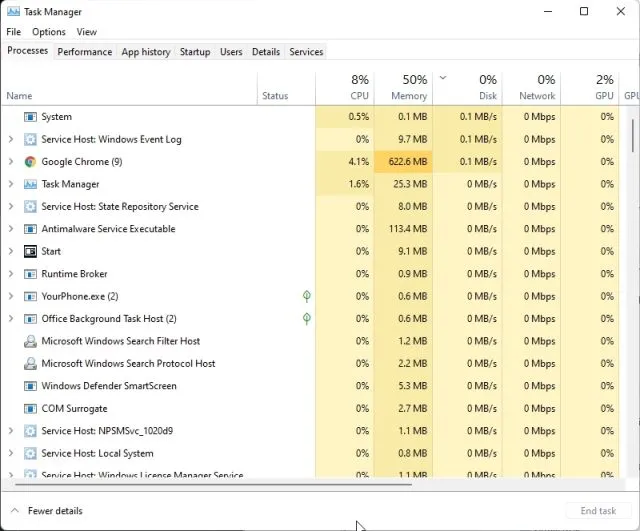
High disk usage is typically indicated in the Task Manager, where the disk column shows 100% activity. This can be caused by various factors, including Windows services, third-party applications, or even malware.
Identifying Background Processes
One of the primary causes of 100% disk usage is the excessive activity of background processes. These processes can range from Windows updates to third-party applications running in the background. To identify these processes:
- Open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc.
- Navigate to the Processes tab and sort by the Disk column.
- Identify any processes consuming a high percentage of disk resources.
Once identified, you can decide whether to end these processes or investigate further. Some processes, like Windows Search or Superfetch, are known to cause high disk usage and can be disabled if necessary.
Updating Drivers
Outdated or corrupted drivers can also lead to high disk usage. Drivers are essential for hardware communication, and outdated versions can cause inefficiencies. To update your drivers:
- Open Device Manager by right-clicking on the Start menu and selecting it from the list.
- Expand the Disk drives section and right-click on your disk drive.
- Select Update driver and follow the on-screen instructions.
Regularly updating drivers ensures that your hardware operates efficiently, reducing the likelihood of high disk usage.
Optimizing System Settings
Windows 11 includes several settings that can be optimized to reduce disk usage. These settings control how the system manages resources and can be adjusted to improve performance. Key settings to consider include:
- Disabling Windows Search: This service indexes files for faster searches but can cause high disk usage. Disable it by typing services.msc in the Run dialog, locating Windows Search, and setting it to Disabled.
- Adjusting Virtual Memory: Virtual memory uses disk space as additional RAM. Adjusting its settings can reduce disk usage. Navigate to System Properties, select Advanced system settings, and under Performance, click Settings. Go to the Advanced tab and adjust the virtual memory settings.
Optimizing these settings can significantly reduce disk usage and improve overall system performance.
Scanning for Malware
Malware can cause high disk usage by running malicious processes in the background. Regularly scanning your system for malware is crucial. Use a reputable antivirus program to perform a full system scan and remove any detected threats.
Additionally, ensure that your antivirus software is up to date to protect against the latest threats. Malware can often mimic legitimate processes, making it essential to use comprehensive scanning tools.
Disabling Unnecessary Startup Programs
Startup programs can contribute to high disk usage by launching automatically when your system boots. Disabling unnecessary startup programs can free up resources and reduce disk activity. To manage startup programs:
- Open Task Manager and navigate to the Startup tab.
- Review the list of programs and disable those that are not essential by right-clicking and selecting Disable.
Reducing the number of startup programs can lead to faster boot times and lower disk usage.
Performing Disk Cleanup
Over time, your system accumulates temporary files and other unnecessary data that can contribute to high disk usage. Performing a disk cleanup can help free up space and reduce disk activity. To perform a disk cleanup:
- Open Disk Cleanup by typing it in the Start menu search bar.
- Select the drive you want to clean and click OK.
- Review the list of files to delete and select those you wish to remove.
Regular disk cleanups can help maintain optimal disk performance and prevent high disk usage.