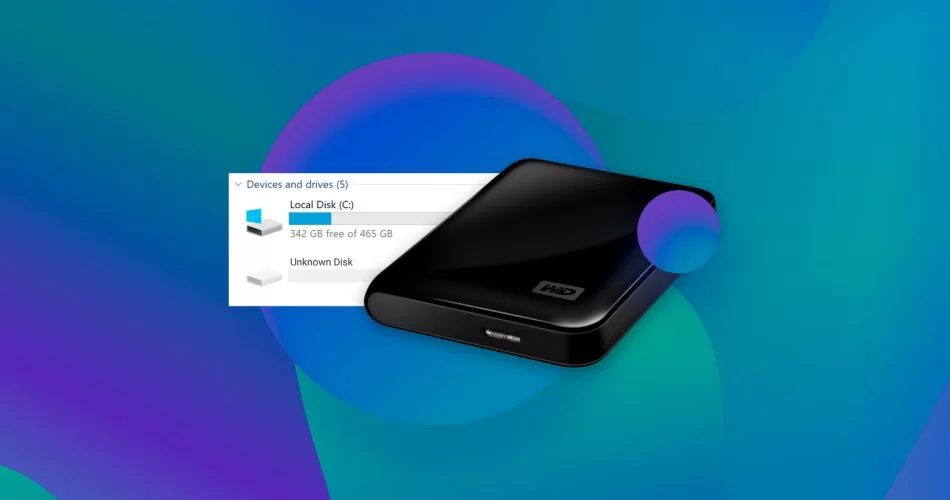
When an external drive fails to appear on your Windows PC, it can be a frustrating experience, especially if you rely on it for important data storage or backups. This issue can stem from a variety of causes, ranging from simple connection problems to more complex driver or hardware failures.
External drives, such as USB flash drives, external SSDs, or HDDs, are widely used for their portability and convenience. However, their reliance on physical connections and software drivers makes them susceptible to connectivity issues. Common storage connectivity issues often arise due to outdated drivers, faulty cables, or incorrect system settings.
Check Physical Connections
Before diving into software troubleshooting, it’s essential to rule out any physical issues. A loose or damaged cable is one of the most common reasons why an external drive may not be detected. Start by inspecting the USB cable or adapter connecting the drive to your PC. Look for signs of wear, such as frayed wires or bent connectors.
If the cable appears damaged, try using a different one. Additionally, test the external drive on another USB port or even another computer. This helps determine whether the issue lies with the drive itself or the port on your PC. Always ensure the drive is properly connected and powered, as some external drives require additional power sources.
Update or Reinstall Drivers
Driver issues are another frequent cause of external drive detection problems. Windows relies on drivers to communicate with hardware devices, and outdated or corrupted drivers can prevent your PC from recognizing the external drive. To address this, you can update or reinstall the necessary drivers.
To update drivers, follow these steps:
- Open the Device Manager by pressing Windows + X and selecting it from the menu.
- Expand the Disk drives section and locate your external drive.
- Right-click the drive and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for drivers and follow the on-screen instructions.
If updating the driver doesn’t work, you may need to uninstall and reinstall it. Right-click the drive in Device Manager, select Uninstall device, and then restart your PC. Windows will automatically reinstall the driver upon reboot.
Assign a Drive Letter
Sometimes, an external drive may not appear in File Explorer because it hasn’t been assigned a drive letter. This can happen if the drive was previously connected to another system or if the drive letter was manually removed. To assign a drive letter, follow these steps:
- Press Windows + X and select Disk Management.
- Locate your external drive in the list. It should appear as unallocated or without a drive letter.
- Right-click the drive and select Change Drive Letter and Paths.
- Click Add, choose a drive letter, and click OK.
This process ensures that the drive is recognized by the operating system and accessible through File Explorer.
Check for Drive Errors
If the external drive is still not showing up, it may contain errors that prevent it from being detected. Windows includes built-in tools to scan and repair drive errors. To use this feature, follow these steps:
- Open This PC in File Explorer.
- Right-click the external drive and select Properties.
- Go to the Tools tab and click Check under the Error Checking section.
- Follow the prompts to scan and repair any issues.
This tool can fix file system errors and bad sectors, which may resolve the detection problem.
Enable the Drive in BIOS/UEFI
In rare cases, the external drive may not be recognized because it’s disabled in the system’s BIOS or UEFI settings. This is more common with internal drives but can also affect external drives connected via certain ports. To check this, restart your PC and enter the BIOS/UEFI settings (usually by pressing F2, Delete, or another key during startup).
Navigate to the Storage or Boot section and ensure that the external drive is enabled. Save any changes and exit the BIOS/UEFI. This step ensures that the drive is recognized at the hardware level.