Windows Firewall is a built-in security feature in Microsoft Windows operating systems designed to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a barrier between your computer and potential threats from the internet or other networks. By default, Windows Firewall is configured to block unauthorized access while allowing legitimate traffic. However, there are instances where it might mistakenly block applications that you intend to use, leading to connectivity issues.
Why Applications Get Blocked by Windows Firewall
Applications can be blocked by Windows Firewall for several reasons. First, the firewall might not recognize the application as safe, especially if it’s newly installed or updated. Second, the application might require specific network ports to function, and if these ports are blocked, the app won’t work as intended. Finally, user-defined firewall rules or third-party security software might interfere with the application’s network access.
Step-by-Step Guide to Check if Windows Firewall is Blocking an App
To determine whether Windows Firewall is blocking an application, follow these steps:
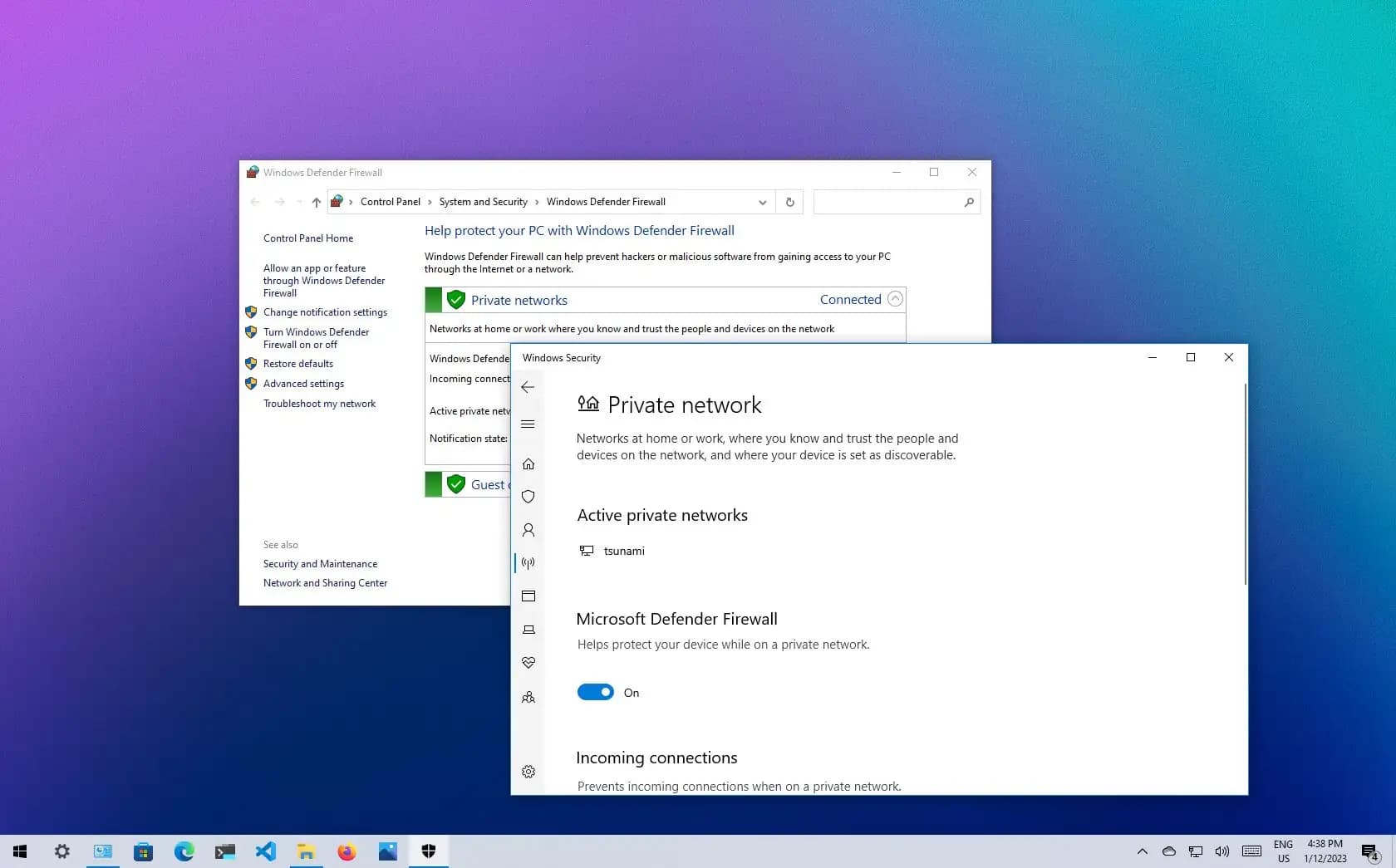
- Open Windows Security: Navigate to the Start menu, search for “Windows Security,” and open the app.
- Access Firewall Settings: Click on “Firewall & network protection” from the left-hand menu.
- Check App Permissions: Scroll down and select “Allow an app through firewall.” This will display a list of applications and their current permissions.
- Verify the Application: Look for the app in question. If it’s listed, ensure that both “Private” and “Public” checkboxes are checked. If it’s not listed, click “Allow another app” to add it manually.
This process allows you to review and modify the firewall rules for specific applications, ensuring they have the necessary permissions to access the network.
Adjusting Firewall Rules for Specific Applications
If you find that an application is blocked, you can adjust the firewall rules to allow it. Here’s how:
- Add the Application: In the “Allowed apps” window, click “Allow another app” and browse to the executable file of the application you want to allow.
- Set Network Types: After adding the app, ensure that the appropriate network types (Private or Public) are selected. Private networks are typically used for home or work environments, while Public networks are for less secure locations like cafes or airports.
- Save Changes: Click “OK” to save your changes and exit the settings window.
By customizing these settings, you can ensure that the application has the necessary access while maintaining overall network security.
Using Advanced Firewall Settings for Detailed Control
For users who require more granular control over firewall settings, Windows provides an advanced interface. To access it:
- Open Control Panel: Search for “Control Panel” in the Start menu and open it.
- Navigate to Advanced Settings: Go to “System and Security” > “Windows Defender Firewall” > “Advanced settings.”
- Create Custom Rules: In the advanced settings window, you can create inbound or outbound rules for specific applications, ports, or IP addresses.
This method is particularly useful for IT professionals or advanced users who need to configure complex network security policies.
Common Network Security Troubleshooting Tips
If adjusting firewall settings doesn’t resolve the issue, consider the following troubleshooting steps:
- Check for Conflicting Software: Ensure that no other security software is interfering with the application’s network access.
- Update the Application: Make sure the application is up to date, as outdated versions might have compatibility issues with the firewall.
- Test on a Different Network: Verify if the issue persists on another network to rule out network-specific problems.