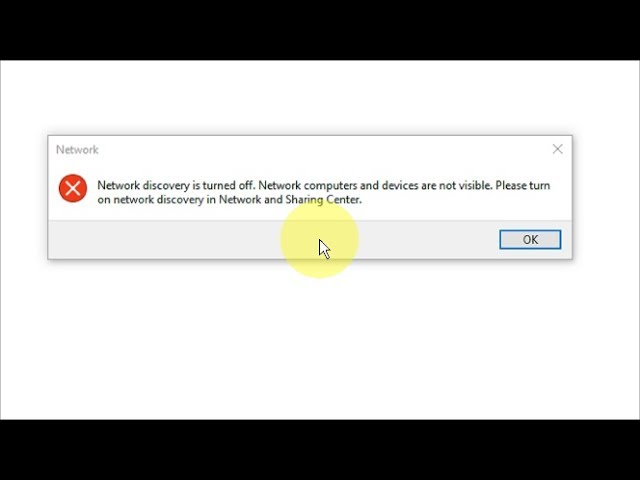
When attempting to share files, printers, or other resources across a network, you may encounter the error message ‘Network Discovery is Turned Off’. This issue typically arises when Windows is unable to detect other devices on the same network, hindering seamless communication. Network Discovery is a crucial feature that allows your computer to find and interact with other devices, making it essential for both home and professional environments.
This error can occur due to misconfigured network settings, disabled services, or even firewall restrictions.
Step 1: Verify Network Profile Settings
Windows uses network profiles to determine the level of access and security for connected networks. There are three primary profiles: Public, Private, and Domain. Network Discovery is typically disabled on Public networks for security reasons, so ensuring your network is set to Private is essential.
To check your network profile, navigate to Settings > Network & Internet > Status. Under the ‘Network profile’ section, ensure the network is set to Private. If it’s set to Public, click on the network name and change the profile to Private. This adjustment allows Windows to enable Network Discovery and share resources securely.
Step 2: Enable Network Discovery in Advanced Sharing Settings
Once your network profile is correctly configured, the next step is to enable Network Discovery in the Advanced Sharing Settings. To do this, open the Control Panel and navigate to Network and Sharing Center > Change advanced sharing settings.
Under the Private network profile, locate the Network Discovery section and select Turn on network discovery. Additionally, ensure that File and printer sharing is enabled. These settings allow your device to detect other computers and share resources seamlessly.
Step 3: Check Network-Related Services
Network Discovery relies on specific Windows services to function correctly. If these services are disabled or not running, you may encounter the error. The key services include Function Discovery Resource Publication, SSDP Discovery, and UPnP Device Host.
To verify these services, press Win + R, type services.msc, and press Enter. In the Services window, locate the aforementioned services and ensure their Startup type is set to Automatic. If any service is stopped, right-click on it and select Start. Restart your computer to apply these changes.
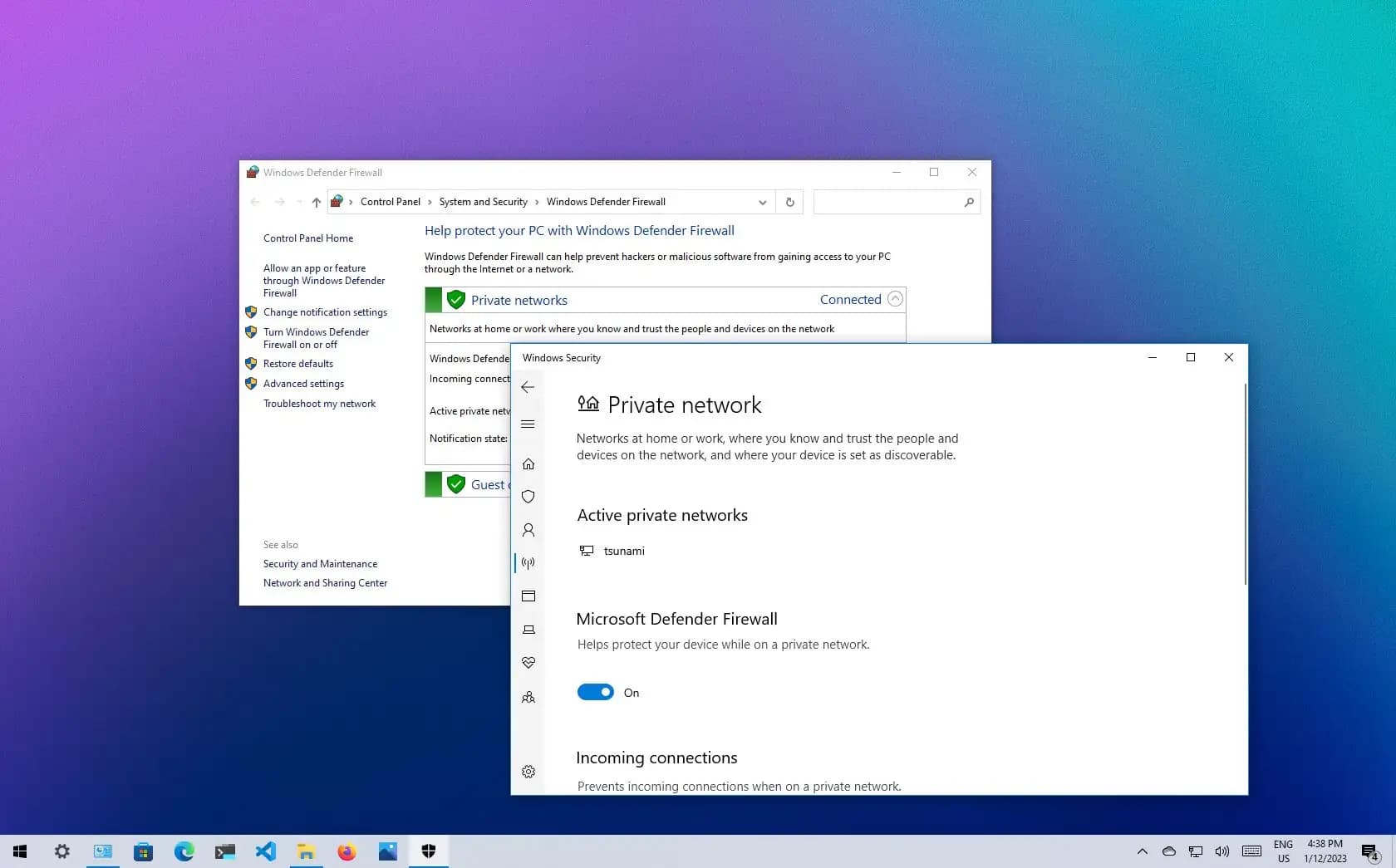
Step 4: Configure Firewall and Antivirus Settings
Firewalls and antivirus programs are designed to protect your system, but they can sometimes block Network Discovery. To resolve this, you need to ensure that the necessary ports and protocols are allowed through your firewall.
Open the Windows Defender Firewall settings and navigate to Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall. Ensure that Network Discovery is checked for both Private and Public networks. If you’re using a third-party antivirus, consult its documentation to allow network-related traffic.
Step 5: Verify Device Connectivity
Even with Network Discovery enabled, connectivity issues can persist if devices are not properly connected to the network. Start by ensuring that all devices are connected to the same network. Use the Command Prompt to ping other devices by typing ping [IP address] and checking for responses.
If devices are not responding, restart your router and modem to refresh the network connection. Additionally, ensure that all devices have unique names and IP addresses to avoid conflicts. These steps can help resolve underlying connectivity issues that may be affecting Network Discovery.
Step 6: Update Network Drivers and Windows
Outdated network drivers or Windows updates can also cause Network Discovery to malfunction. To update your network drivers, open Device Manager, expand the Network adapters section, right-click on your adapter, and select Update driver.
For Windows updates, navigate to Settings > Update & Security > Windows Update and click Check for updates. Installing the latest updates ensures compatibility and resolves known bugs that may be affecting Network Discovery.