Modern computing relies heavily on the efficient utilization of hardware resources, particularly the CPU. In Windows 11, enabling all CPU cores can significantly enhance system performance, especially for resource-intensive tasks such as gaming, video editing, and software development. This guide provides a detailed, step-by-step explanation of how to enable all CPU cores in Windows 11, covering both BIOS/UEFI settings and operating system configurations.
Understanding CPU Cores and Their Importance
CPU cores are individual processing units within a central processing unit (CPU). Each core can handle its own tasks independently, allowing for parallel processing. Modern CPUs often come with multiple cores, such as quad-core, hexa-core, or even octa-core processors. Enabling all CPU cores ensures that your system can distribute workloads efficiently, reducing bottlenecks and improving overall performance.
By default, Windows 11 is designed to utilize all available CPU cores. However, certain system configurations or BIOS/UEFI settings may limit the number of active cores. This can occur due to power-saving features, incorrect settings, or hardware limitations. Ensuring that all cores are enabled is crucial for maximizing your system’s potential.
Accessing BIOS/UEFI Settings
The BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is firmware used to perform hardware initialization during the booting process and to provide runtime services for operating systems. To enable all CPU cores, you may need to access and modify settings in the BIOS/UEFI.
To access the BIOS/UEFI, restart your computer and press the designated key (often F2, F10, DEL, or ESC) during the boot process. The specific key varies depending on your motherboard manufacturer. Once inside the BIOS/UEFI interface, navigate to the ‘Advanced’ or ‘CPU Configuration’ section. Look for settings related to CPU cores, such as ‘Core Multi-Processing’ or ‘Number of Active Cores.’ Ensure that all cores are enabled and save your changes before exiting.
Configuring Windows 11 for Optimal CPU Core Usage
After ensuring that all CPU cores are enabled in the BIOS/UEFI, you may need to configure Windows 11 to utilize them effectively. Open the ‘System Configuration’ utility by typing ‘msconfig’ in the Run dialog (Win + R). Navigate to the ‘Boot’ tab and click on ‘Advanced options.’ Check the box for ‘Number of processors’ and select the maximum number of cores available. Click ‘OK’ and restart your computer to apply the changes.
Additionally, you can use the Task Manager to monitor CPU core usage. Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc to open Task Manager, then go to the ‘Performance’ tab. Under ‘CPU,’ you should see a graph for each core. If all cores are active, you will see multiple graphs indicating that your system is utilizing all available processing power.
Power Settings and CPU Core Management
Windows 11 includes power plans that can affect CPU core usage. To ensure optimal performance, navigate to ‘Control Panel’ > ‘Hardware and Sound’ > ‘Power Options.’ Select the ‘High performance’ power plan or create a custom plan that prioritizes performance over energy savings. This ensures that your CPU cores remain active and ready to handle demanding tasks.
You can also adjust advanced power settings to fine-tune CPU core behavior. Under ‘Processor power management,’ set the ‘Minimum processor state’ to 100% and the ‘Maximum processor state’ to 100%. This prevents the system from throttling CPU cores, ensuring consistent performance.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
If you encounter issues after enabling all CPU cores, such as system instability or overheating, it may be necessary to revert some changes. Overclocking or enabling too many cores without adequate cooling can lead to thermal throttling or hardware damage. Ensure that your system has proper cooling and that your power supply can handle the increased load.
Additionally, check for BIOS/UEFI updates from your motherboard manufacturer. Firmware updates can resolve compatibility issues and improve system stability. If problems persist, consider consulting with a hardware specialist or referring to your motherboard’s manual for further guidance.
Advanced Techniques for Performance Optimization
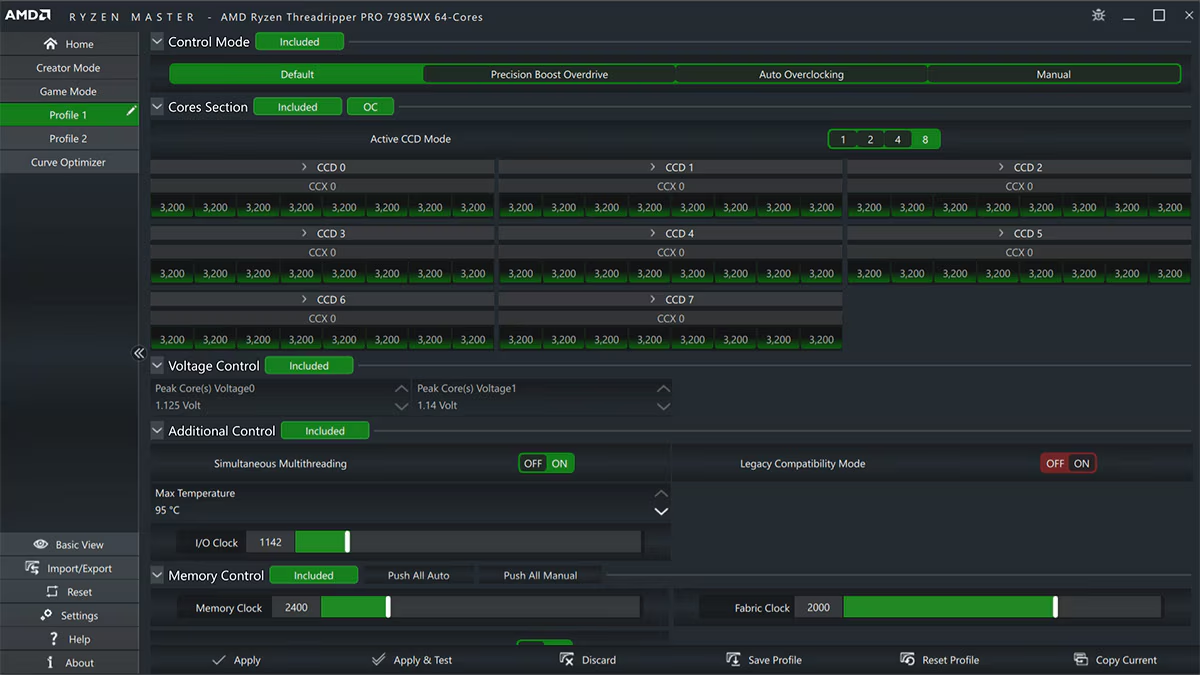
For advanced users, additional techniques can further optimize CPU core usage. Tools like Intel’s Extreme Tuning Utility (XTU) or AMD’s Ryzen Master allow for fine-tuning CPU settings, including core activation, clock speeds, and voltage. These tools provide granular control over your processor, enabling you to achieve maximum performance for specific workloads.
Another technique is to use third-party software to monitor and manage CPU cores. Applications like CPU-Z or HWMonitor provide detailed information about your CPU’s performance and can help identify bottlenecks. By analyzing this data, you can make informed decisions about further optimizations.