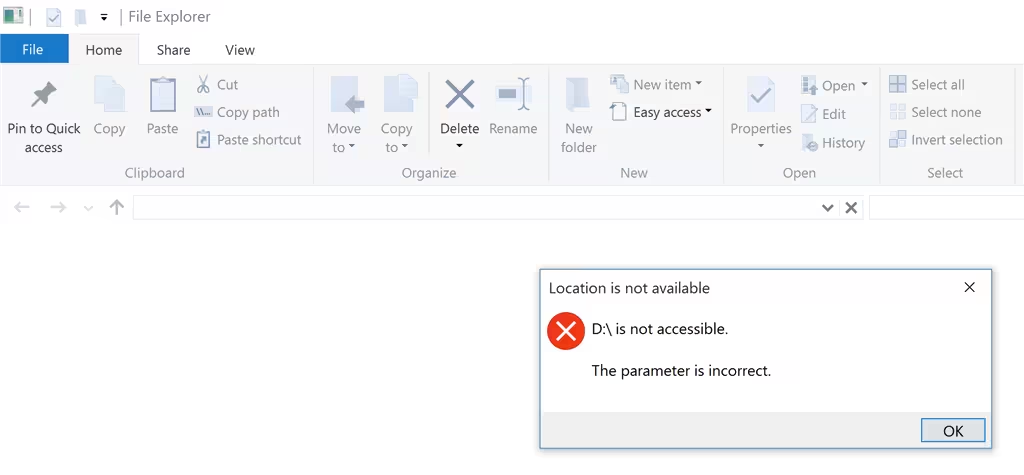
When working with files or drives on Windows, encountering the error message “The parameter is incorrect and is not accessible” can disrupt your workflow. This error typically arises due to file system corruption, permission issues, or outdated drivers. Resolving it requires a systematic approach, including checking file permissions, running system file checks, and ensuring your drivers are up to date.
Check File and Folder Permissions
File and folder permissions play a critical role in accessing data on Windows. If the permissions are misconfigured, you may encounter the “The parameter is incorrect” error. To verify and adjust permissions:
- Right-click the file or folder causing the issue and select Properties.
- Navigate to the Security tab and click Edit to modify permissions.
- Ensure your user account has Full Control or at least Read & Execute permissions.
- Click Apply and OK to save changes.
If the issue persists, consider taking ownership of the file or folder. Right-click the item, select Properties, go to the Security tab, and click Advanced. Under the Owner section, change the owner to your user account and apply the changes.
Run the System File Checker (SFC)
Corrupted or missing system files can trigger the “The parameter is incorrect” error. The System File Checker (SFC) is a built-in Windows tool that scans and repairs system files. To run SFC:
- Open the Command Prompt as an administrator by searching for cmd in the Start menu, right-clicking, and selecting Run as administrator.
- Type sfc /scannow and press Enter.
- Wait for the scan to complete. If any issues are found, SFC will attempt to repair them automatically.
After the process finishes, restart your computer and check if the error is resolved. If SFC cannot fix the issue, you may need to run the Deployment Imaging Service and Management Tool (DISM) to repair the Windows image.
Update or Reinstall Device Drivers
Outdated or incompatible drivers can also cause the “The parameter is incorrect” error, especially when accessing external drives or hardware. To update your drivers:
- Press Windows + X and select Device Manager.
- Expand the relevant category (e.g., Disk drives or Universal Serial Bus controllers).
- Right-click the device and select Update driver.
- Choose Search automatically for drivers and follow the on-screen instructions.
If updating the driver does not resolve the issue, consider uninstalling and reinstalling it. Right-click the device in Device Manager, select Uninstall device, and restart your computer. Windows will automatically reinstall the driver upon reboot.
Check for Disk Errors
File system errors on your disk can lead to accessibility issues. Windows includes a utility called Check Disk (CHKDSK) to scan and repair disk errors. To use CHKDSK:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type chkdsk /f /r X: (replace X with the drive letter) and press Enter.
- If the drive is in use, you will be prompted to schedule the scan for the next restart. Type Y and press Enter.
- Restart your computer to begin the scan.
CHKDSK will scan the drive for errors and attempt to fix them. This process can take some time, depending on the size and condition of the drive.
Verify External Drive Compatibility
If the error occurs when accessing an external drive, compatibility issues may be the cause. Ensure the drive is formatted with a file system supported by Windows, such as NTFS or exFAT. To check the file system:
- Connect the external drive to your computer.
- Open File Explorer, right-click the drive, and select Properties.
- Under the General tab, check the File system type.
If the drive uses an unsupported file system, back up your data and reformat it to NTFS or exFAT. Note that reformatting will erase all data on the drive.
Disable Write Protection
Write protection on a drive or file can prevent access and trigger the error. To disable write protection:
- Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
- Type diskpart and press Enter.
- Type list disk to display all connected drives.
- Select the drive by typing select disk X (replace X with the disk number).
- Type attributes disk clear readonly and press Enter.
This command removes the read-only attribute from the drive, allowing you to access and modify its contents.