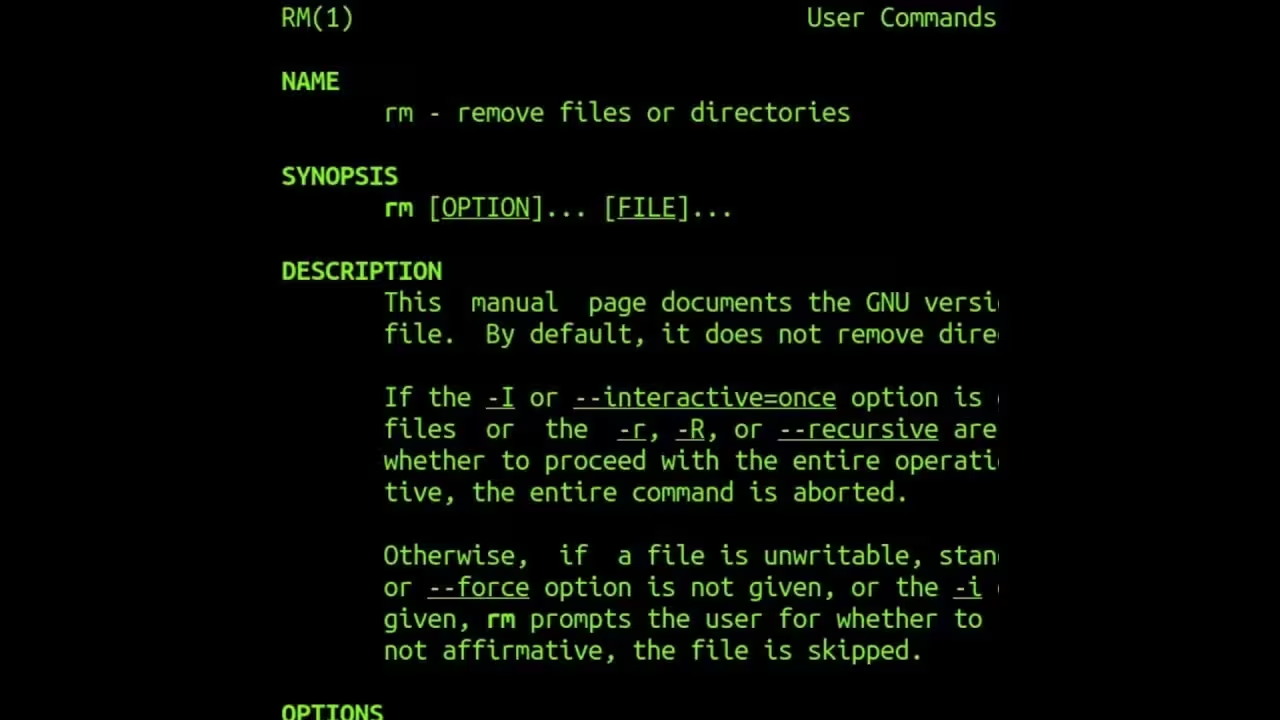
The rmdir command in Linux is used to remove empty directories from the filesystem. Unlike the rm -r command (which deletes directories and their contents recursively), rmdir only works if the directory is empty. This makes it a safer option for cleaning up directories without risking accidental data loss.
- Remove a Single Empty Directory
- Remove Multiple Empty Directories
- Remove Nested Empty Directories
- Verbose Mode (Show Deletion Progress)
- Ignore Non-Empty Directory Errors
- Remove Directories with Spaces
- Remove Directories with Special Characters
- Delete Empty Directories via Wildcards
- Combine with find to Remove All Empty Directories
- Force-Delete Empty Directories (No Error for Non-Empty)
- Redirect Errors to a File
- Use Absolute Paths
- Remove Hidden Directories
- Check Directory Status Before Deletion
- Use rmdir in Scripts Safely
It’s particularly useful in scripts or workflows where you need to ensure directories are empty before deletion. If a directory contains files or subdirectories, rmdir will throw an error, prompting you to address the contents first.
Remove a Single Empty Directory
rmdir dirname
Deletes the empty directory dirname if it exists.
Remove Multiple Empty Directories
rmdir dir1 dir2 dir3
Deletes dir1, dir2, and dir3 if they are all empty.
Remove Nested Empty Directories
rmdir -p parent/child/grandchild-premoves the entire directory path if all directories in the path are empty.- Deletes
grandchild, thenchild, thenparent(if empty).
Verbose Mode (Show Deletion Progress)
rmdir -v empty_dir-vprints a confirmation message:rmdir: removing directory 'empty_dir'.
Ignore Non-Empty Directory Errors
rmdir --ignore-fail-on-non-empty dirname- Suppresses errors if
dirnameis not empty. - Useful in scripts to avoid interruptions.
Remove Directories with Spaces
rmdir "My Folder"
Use quotes to delete directories with spaces in their names.
Remove Directories with Special Characters
rmdir 'dir$name' # Use quotes
rmdir dir\#name # Use backslash to escape
Handles names containing $, #, or other special characters.
Delete Empty Directories via Wildcards
rmdir prefix_*
Deletes empty directories matching the wildcard pattern (e.g., prefix_1, prefix_2).
Combine with find to Remove All Empty Directories
find . -type d -empty -exec rmdir {} \;findlocates all empty directories in the current tree.rmdirdeletes them one by one.
Force-Delete Empty Directories (No Error for Non-Empty)
rmdir -p --ignore-fail-on-non-empty path/to/dir
Combines -p and --ignore-fail-on-non-empty for silent cleanup attempts.
Redirect Errors to a File
rmdir dirname 2> errors.log
Saves error messages (e.g., “Directory not empty”) to errors.log.
Use Absolute Paths
rmdir /home/user/empty_dir
Specifies the full path to the directory for precise deletion.
Remove Hidden Directories
rmdir .hidden_dir
Deletes hidden directories (names starting with .).
Check Directory Status Before Deletion
ls -d dirname/ && rmdir dirname
Lists the directory first to confirm it exists and is empty.
Use rmdir in Scripts Safely
if [ -d "dirname" ] && [ -z "$(ls -A dirname)" ]; then
rmdir dirname
fi
Checks if dirname exists and is empty before deleting.
Key Notes:
- Safety First:
rmdirwill not delete directories with files/subdirectories. Userm -rfor non-empty directories (with caution!). - Permissions: Ensure you have write access to the directory and its parent.
- Alternatives: For non-empty directories, use
rm -rf dirname(but double-check the path!).