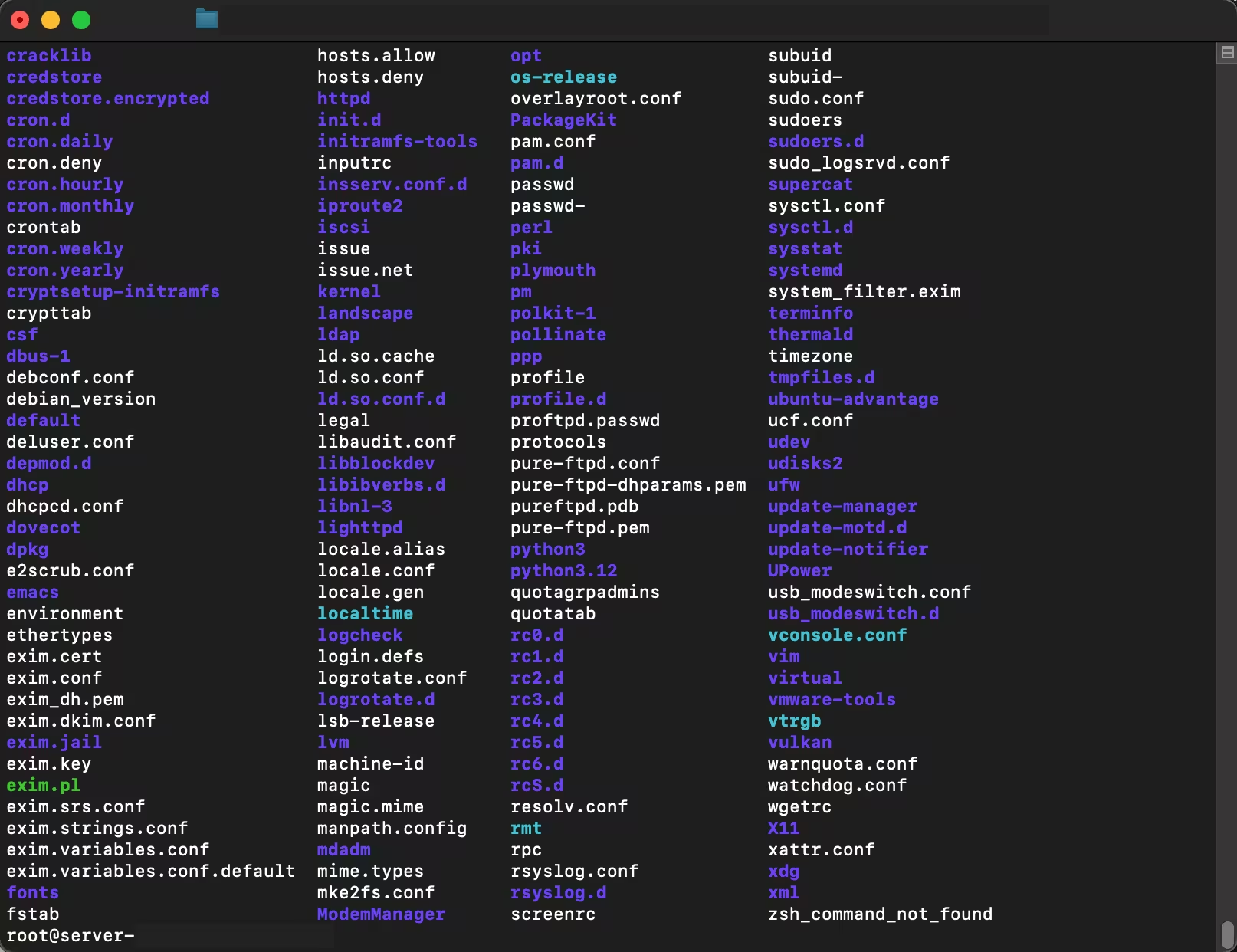
1. List Files in Current Directory
lsLists all visible files and directories in the current folder.
- 1. List Files in Current Directory
- 2. Detailed List (Long Format)
- 3. Show Hidden Files
- 4. Combine -l and -a
- 5. Human-Readable File Sizes
- 6. Sort by Modification Time
- 7. Reverse Sort Order
- 8. List Files in a Specific Directory
- 9. Recursive Listing
- 10. Filter by File Extension
- 11. Display Inode Numbers
- 12. Append File Type Indicators
- 13. Sort by File Size
- 14. Show Directory Itself (Not Contents)
- 15. Comma-Separated Output
- 16. Show Numeric UID/GID
- 17. One Entry Per Line
- 18. Colorized Output
- 19. Sort by Access Time
- 20. Get Help
- Pro Tip: Combine Flags
2. Detailed List (Long Format)
ls -lShows permissions, owner, size, and modification time in columns.
3. Show Hidden Files
ls -aIncludes hidden files (those starting with ., like .bashrc).
4. Combine -l and -a
ls -laDetailed list including hidden files.
5. Human-Readable File Sizes
ls -lhDisplays sizes in KB, MB, or GB (e.g., 4.0K instead of 4096).
6. Sort by Modification Time
ls -ltNewest files appear first.
7. Reverse Sort Order
ls -lrReverse the default sorting (e.g., alphabetical Z → A).
8. List Files in a Specific Directory
ls /var/logList contents of /var/log instead of the current directory.
9. Recursive Listing
ls -RLists all files and subdirectories recursively.
10. Filter by File Extension
ls *.txtLists only files ending with .txt.
11. Display Inode Numbers
ls -iShows the inode number (unique identifier) for each file.
12. Append File Type Indicators
ls -FAdds symbols like / for directories and * for executables.
13. Sort by File Size
ls -lSLargest files appear first.
14. Show Directory Itself (Not Contents)
ls -d */Lists only directories in the current location.
15. Comma-Separated Output
ls -mDisplays files as a comma-separated list: file1, file2, dir1.
16. Show Numeric UID/GID
ls -nDisplays user/group IDs instead of names (useful for scripting).
17. One Entry Per Line
ls -1Forces single-column output (helpful for parsing).
18. Colorized Output
ls --color=autoHighlights directories, executables, and symlinks in color.
19. Sort by Access Time
ls -luSorts by last access time instead of modification time.
20. Get Help
ls --helpDisplays all available ls options and flags.
Pro Tip: Combine Flags
ls -lath-l: Long format-a: Show hidden files-t: Sort by time-h: Human-readable sizes
This shows all files in a detailed, time-sorted list with readable sizes.
Master these to navigate and manage files efficiently in Linux! 🐧